Combat CTE Mismatch with Constant Force-Load Washers
CTE mismatch is the difference in multiple material’s thermal expansion and contraction rates. At ALLVAR, we pride ourselves in solving tough thermal problems with new solutions. When we were told that thermal expansion created problems for bolted joints, we decided to tackle the problem with Negative Thermal Expansion ALLVAR Alloy 30.
Background
The difference in thermal expansion between bolt and clamp material causes bolts to lose their clamping force, leading tests to fail and hours of rework. To solve this CTE mismatch problem, we developed a new type of washer. We call them constant force-load washers. These washers expand while other components contract, combating CTE mismatch (the difference in thermal expansion coefficients between multiple components).
CTE Mismatch and Preloads in Bolted Joints
CTE mismatch occurs when the Coefficients of Thermal Expansion (CTEs) of two materials are different. Using a torque requirement to install bolts can lead to clamping force uncertainty. Stacking thermal expansion mismatch on top of this uncertainty can easily push a joint out of specification. When operating at wide temperatures, this CTE mismatch can lead to a loss of preload or overloading. That is when things go wrong. When designing joints, an appropriate preload is often specified for a particular design. Not only do bolts have to be torqued to the correct preload, but preload must be maintained within a certain margin of safety through the bolt’s operational life. If the preload drifts beyond that margin, there is a risk that the bolt will loosen and subsequently fail to maintain the constant force leading to loss of usefulness or complete failure.
ALLVAR’s negative thermal expansion washers offer a new method to maintain a consistent preload, from extreme cryogenic temperatures to 100°C.
Tackling CTE Mismatch – One Washer at a Time
The CTE mismatch problem inspired ALLVAR founder and material scientist Dr. James A. Monroe to create a bolted joint simulation to explore the effects of swapping out a stainless-steel washer for an ALLVAR Alloy 30 washer.
As the temperature of a loaded bolt changes, so does the stress in the bolt and thus the clamping force. A thermal load is induced because the thermal expansion of the materials in the bolted joint are not the same, causing the aluminum to expand more than the stainless-steel bolt. In a normal joint assembly, like one using a stainless-steel washer, the joint loosens as the temperature cools, quickly losing clamping force. As the temperature of the joint increases, so does the tension in the bolt. This increasing thermal load causes an increase in the internal stresses on the bolt. The joint loading increases with temperature and loses clamping force as temperatures cool.
In the GIF above, the left bolted joint is held with a stainless-steel washer. We see the bolt stress rise towards 365 MPa as the temperature increases from 25°C to 100°C. When cooling to extreme temperatures, we see the opposite effect, the bolt stress and resulting clamping force drops dramatically – from 338 MPa at 25°C to 263 MPa at -200°C. This results in 22% less clamping force.
The Negative Thermal Expansion Solution
Swapping out the top M5 washer in the bolted joint for an ALLVAR Alloy 30 washer greatly diminishes the loss in bolt tension. In the FEA analysis gif, we see very little change in bolt tension between -200°C, 25°C, and 100°C. This is due to ALLVAR Alloy 30’s negative thermal expansion property (-30 ppm/°C at 25°C), which is compensating for the difference in expansion between the aluminum plates (23.6 ppm/°C) and stainless-steel bolt (16.3ppm/°C).
Assuming the bolt was torqued to an ideal preload of 338 MPa at room temperature, we can compare the effect of the CTE mismatch for each bolted joint. The uncompensated joint changes preload wildly with temperature change and is easily pushed out of the +/- 10% preload margins. On the other hand, the ALLVAR Alloy 30 washer varies only slightly across the 300°C temperature window.
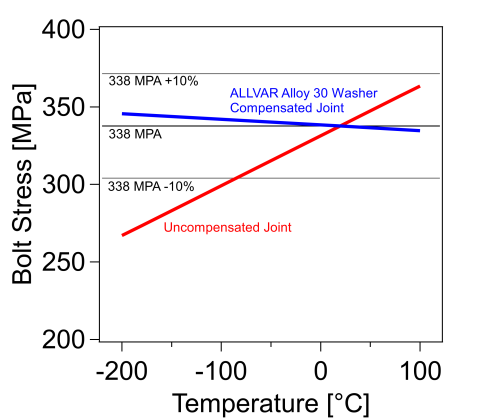
The bolt stress is now nearly constant across temperature. ALLVAR Alloy 30 constant force washers improve reliability by limiting clamping force variation that leads to fatigue, loosening, and degradation of the joint.
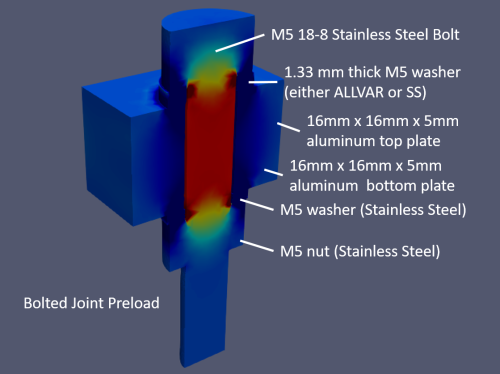
Bolted Joint Components and Assumptions
The bolted joint consists of the following:
- 1x M5 18-8 stainless steel bolt
- 1x 1.33mm M5 stainless steel or ALLVAR Alloy 30 washer
- 2x 5mm thick aluminum plates. One top and one bottom plate. The width for this analysis is 16mmx16mm.
- 1x M5 stainless steel washer
- 1x M5 stainless steel nut
Engineering Assumptions:
- Linear Elastic Isotropic mechanical properties.
- No change in elastic modulus or other elastic properties with temperature.
- No change in thermal expansion magnitudes with temperature.
- Thermal expansion anisotropy taken into consideration for ALLVAR Alloys. All other materials have isotropic thermal expansion.
- No slip or friction condition. All interfaces are considered bonded.
- Bolt preloaded to 70% of its yield strength for an 18-8 stainless steel bolt.
Applications and further learning
ALLVAR Alloy 30 constant-force washers and spacers directly combat the CTE mismatch in bolted joints. Whether your application is in cryogenics, optics, defense, energy, or industrial processing, ALLVAR Alloy 30 can improve the safety and reliability of your joints between cryogenic temperatures and 100°C. Still want to learn more? Please visit our washer page here. If you are interested in pricing information, please use the contact button below.
Don’t forget to follow ALLVAR on our LinkedIn page, check out our YouTube page, and subscribe to our newsletter to stay up to date with our latest news and events! As a team of passionate material scientists and engineers, we would love to connect and answer any questions you may have about our revolutionary material.
Other Washer-related Posts

CTE Mismatch in Bolted Joints – Negative Thermal Expansion Washers offer a solution!
CTE Mismatch in Bolted Joints challenging your design? Check out how a simple NTE Washer can help maintain constant bolt preloads complete with a FEA

Introductory Guide to Tailored Thermal Expansion
Want to match a certain CTE? The tailored thermal expansion guide has you covered. Learn how negative thermal expansion can help here.

Cryogenic Solutions for Thermal Expansion
A short article about ALLVAR Alloy 30 washer compensated joints in cryogenic environments

Design with Athermal Materials in Solidworks
Athermal Material design is easy with the SOLIDWORKS ALLVAR Alloy 30 material definition. Request the file here and design with negative thermal expansion today!

Thermal Compensating Washers for CTE Mismatch
Learn how to use negative thermal expansion ALLVAR washers or spacers to maintain a constant preload and tackle CTE mismatch.

Thermal compensation washers now available with COTS item numbers!
New commercially-off-the-shelf ALLVAR thermal compensation washer have arrived! Learn more here.






